For most of the Earth’s history, the only rubber available was naturally occurring, found in rubber trees and other plants. But in the past century or so, humans have innovated, creating many different types of rubber by vulcanizing, experimenting with formulas and making good use of petroleum and petroleum byproducts.
What is Rubber?
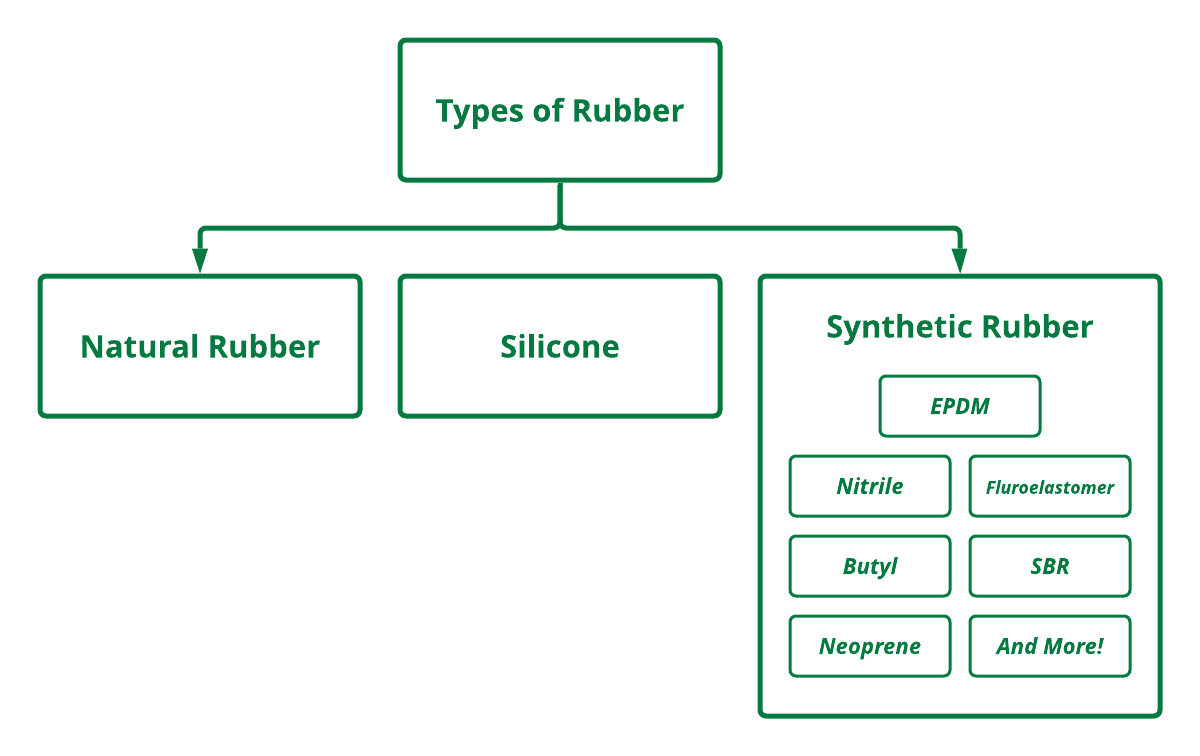
Rubber is a highly stretchy, abrasion resistant material that’s commonly molded into various shapes. It is widely used and has applications in countless components and household items. Often what people fail to understand about rubber is that there’s many different types. The two main categories of rubber are natural rubber and synthetic rubbers. Silicone rubber is often considered to be a third category.
Today, there are many types of rubber, each of which is ideal for different applications. Companies like Custom Rubber Corp. specialize in determining which type will work best for you. But if you need a quick primer on each type of rubber, the following guide will help.
Please note, the many different types of rubber materials can have a wide range of physical characteristics depending on how they are formulated. The properties described in this summary are typical, but not absolute.
What is Natural Rubber?
Natural rubber is a rubber material found in nature. It is produced by tapping trees, similar to maple syrup, not by processing petroleum. The trees produce latex, which is then processed into a usable natural rubber material.

Natural rubber dates back thousands of years to civilizations like the Inca, who would use rubber to make balls for ancient sports. Back then, the biggest downside to natural rubber is that it would start to melt or get sticky when the temperature got too hot. It wasn’t until 1839 that Charles Goodyear invented rubber vulcanization to keep the material stable.
Because natural rubber comes from rubber trees and is not petroleum based, it is on a different branch of the “Rubber Family Tree” so to speak than the synthetic rubbers identified below.
Pros and Cons of Natural Rubber
Natural rubber is the ideal choice for any product that requires high elasticity/tensile strength and abrasion/tear resistance. Natural rubber also has good vibration dampening characteristics and low compression set values. It bonds to a wide variety of substrates.
However, natural rubber’s main disadvantage is twofold: It does not demonstrate high resistance to heat and oils or ozone and UV, and its cost is extremely variable in comparison to synthetic rubbers.
Interested in Learning More About Natural Rubber? Read on Here.
What is Synthetic Rubber?
In contrast to natural rubbers, which come from plants that produce latex, synthetic rubbers are made primarily of petroleum byproducts. These human-made rubbers are oxygen, oil and ozone resistant. They are used primarily for gaskets, seals, O-rings, hoses, flooring, matting, tires, belts and more. Of all the rubbers produced each year in the U.S., around two-thirds are synthetics.
EPDM Rubber

Ethylene propylene diene monomer, or EPDM for short, is one of the commonly used polymers in the rubber molding industry. It is the ideal choice for any product that requires general ozone, chemical and weather resistance. EPDM has good resistance to alcohols, greases, detergents, ketones, silicone oils, and mild acids. It’s also a fairly cost effective material.
These characteristics have contributed to EPDM Rubber’s reputation as one of the most basic and cost-effective materials options. If a product needs to be made from rubber, many manufacturers start with EPDM. EPDM is one of many types of synthetic rubbers
Pros and Cons of EPDM Rubber
EPDM is a great general purpose rubber because of it's excellent resistance properties. It is resistant to weather and ozone, water, detergents, greases, mild acids and silicone oils. It's also versatile, strong, cheap and easy to work with. EPDM is easy to process and comes at a relatively low cost.
Unfortunately, EPDM rubber absorbs oils and can fall apart when used for certain applications. While it is excellent in its resistance to outdoor elements, the main disadvantages of EPDM lay in its resistance to other common materials like petroleum oils, fuel, mineral oils and petroleum-based lubricants. It also has poor tear and abrasion resistance.
Interested in Learning More About EPDM Rubber? Read on Here.
SBR Rubber
SBR (Styrene butadiene) rubber is one of the first synthetic rubber materials ever invented. It has many of the same properties as natural rubber, but is petroleum-based rather than latex-based.
A World War II R&D push eventually established Neoprene and SBR rubbers as usable materials for rubber product production. Today SBR rubber is most often used in combination with natural rubber rather than as a substitute.
_1.png)
Pros and Cons of SBR Rubber
SBR rubber has excellent abrasion characteristics and reasonably good tear and elongation properties. It is resistant to abrasion, tears, electricity, cracks, non-petroleum based fluids, odors and, to an extent, heat. It also has a low compression set.
SBR rubber has disadvantages similar to natural rubber. They both demonstrate poor oil and ozone resistance. SBR rubber also has low tensile strength.
Interested in Learning More About SBR Rubber? Read on Here.
Neoprene Rubber / Chloroprene Rubber
Neoprene rubber is produced by polymerizing Chloroprene. It is the ideal choice for any product that requires petroleum oils and weather resistance. Unlike other rubber materials that do one or the other, Neoprene rubber performs well when exposed to petroleum products but also includes resistance to ozone, UV, and oxygen. Neoprene is also easy to bond to a variety of substrates.
Pros and Cons of Neoprene Rubber
Neoprene rubber’s main advantage is its ability to withstand petroleum-based products and weather conditions. Most rubbers only tolerate one or the other. It also demonstrates excellent bonding to substrates.
Neoprene rubber may be resistant to more elements than other rubber types, but it cannot withstand everything. Its main disadvantages are that it is not resistant to solvents and has only moderate water resistance.
Interested in Learning More About Neoprene? Read on Here.
Nitrile Rubber / NBR Rubber
Nitrile rubber is also called nitrile butadiene rubber, NBR, Buna-N and acrylonitrile butadiene rubber. It is a synthetic rubber, and is usually the ideal choice for any product that requires petroleum (oil or gas) resistance.
This material, like many other synthetic rubbers, gained popularity during World War II when natural rubber resources were in short supply around the globe. Today, Nitrile rubber is used mainly when an application requires a resistance to petroleum. It is a common base for gaskets, O-rings and other types of seals.

Pros and Cons of Nitrile Rubber
Nitrile rubber’s biggest advantage is its resistance to petroleum, but it also has several other desirable properties. It has excellent abrasion resistance, good tear resistance and a low compression set.
However, Nitrile rubber is not ideal in applications that require prolonged exposure to ozone or heat. It is not resistant to these elements or flames and has only a moderate operating temperature range.
Interested in Learning More About Nitrile Rubber? Read on Here.
Butyl Rubber
Butyl rubber is a synthetic rubber valued for its low gas and moisture permeability and vibration dampening. Molded butyl rubber also has good resistance to heat aging, abrasion and tearing, and can be a good electrical insulator.
Pros and Cons of Butyl Rubber
One of the main advantages of butyl rubber is its excellent gas and moisture permeability, but there are several other characteristics that make it a viable option for your needs. It has excellent vibration dampening and resistance to heat, UV and ozone. It also has chemical inertness, meaning it is not reactive when combined with other materials.
The main disadvantage of butyl rubber is its cost. The majority of the time, a similar, less expensive, easier to work rubber material can be used in its place. It is also difficult to process. In terms of performance, it has only a modest working temperature range and demonstrates poor resistance to petroleum.
Interested in Learning More About Butyl Rubber? Read on Here.
Fluoroelastomer Rubber / Viton®
Flouroelastomer rubber - Viton® rubber is the ideal choice for any product that experiences extremes in either temperature or fluid exposure. It is a high performance rubber specifically formulated to withstand these extremes. Flouroelastomers also have low gas permeability. Typical applications include O-rings, seals and gaskets that must withstand aggressive temperature or chemical exposure.

Pros and Cons of Fluoroelastomer Rubber / Viton®
When fluoroelastomers are needed to withstand high temperatures or chemical exposure, they deliver, standing up against temperatures up to 480º F! They have great resistance to temperature and most chemicals as well as UV and ozone.
However, because fluoroelastomers are designed for such specific instances and require extreme tolerance, they are of higher cost than any other rubber material on this list. Aside from this, other disadvantages include poor resistance to hot water and steam and a fairly low temperature flexibility.
Interested in Learning More About Fluoroelastomer Rubber? Read on Here.
Silicone Rubber
Silicone rubber is a third category of rubber all its own that exists outside natural and synthetic rubbers. It is the ideal choice for any product that requires high or low temperature resistance. It is versatile and highly durable. Silicone rubber stays flexible and provides excellent compression set across the entire range of temperatures. These properties combined with its ease of use in manufacturing mean silicone rubber can be found in a wide variety of consumer products. It is also used widely in industries like aerospace, construction, medical and automotive.
Pros and Cons of Silicone Rubber
Silicone rubber has some of the best extreme temperature properties that exist in the world of rubbers. It also has a good compression set and a great tactile feel, making it a good choice for consumer products.
Silicone rubber’s main disadvantage is its tear and abrasion resistance. It has poor abrasion resistance and only fair tear resistance.
Interested in Learning More About Silicone Rubber? Read on Here.
The Different Types of Rubber
This list is robust, but not exhaustive. There are other, lesser used types of rubber available on the market as well. In addition, many of the above rubber types can be combined to optimize certain properties depending on the desired application.
The best way to know which rubber is ideal for your product or need is to consult an expert rubber company. Whether you have a good idea of what you need or are completely in the dark, speaking with an experienced rubber professional will help you identify the path forward.
Contact Custom Rubber Corp. today for answers on all things rubber. Ask a question, get a quote or drop by to say hello here.